Is there a point to language groups and families?
How many languages are there in the world?
This is a common question and with over seven billion people on the planet, it’s one that is worth asking.
While the number of languages can differ according to how one defines language, SIL International has spent more than 80 years cataloguing the world’s living languages and organized the data into a database called Ethnologue. According to the 2017 edition of the database, there are 7,099 languages in existence.
What Exactly Is a Language Family?
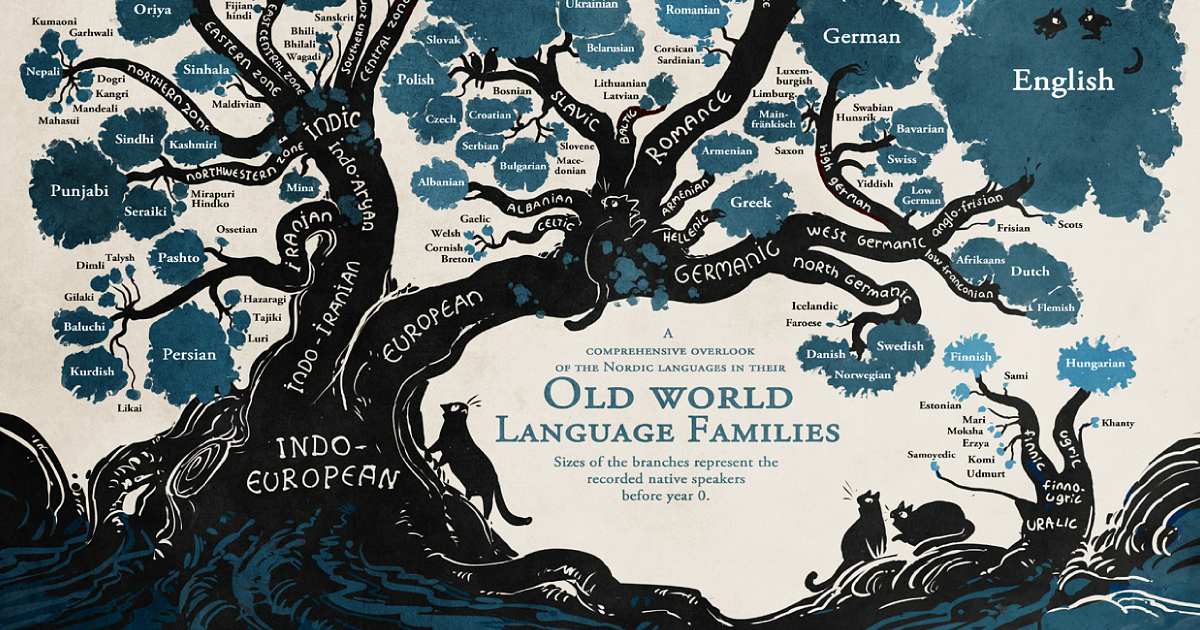
Most of those 7,099 languages belong to language families which are a group of related languages. These groups are developed from their common historic ancestor or proto-language.
How Are Language Relationships Established?
It can easy to establish language relationships. Let’s use the Romance languages as an example:
- Italian is a descendant of Latin which was spoken in Italy 2,000 years ago
- The Roman conquest went on to spread Latin throughout Europe
- Latin in Europe branched out into regional dialects and when the Roman Empire dissolved, the regional dialects evolved into what we know as the Romance languages, including Spanish, French, Portuguese, Romanian, Catalan and Italian
- The regional dialects make up the Romance branch of what we know as the Indo-European language family
Let’s make it easier by using an example. Here, we use the word “water.”
- Portuguese – agua
- Spanish – agua
- Catalan – aigua
- Italian – acqua
- Romanian – apă
Can you see the similarities?
How Are the Language Families Arranged?
The relationship between Latin and its language branches is typical of how language families are organized.
Let’s break it down in a way that is easier to understand:
- An ancestral language gave rise to a number of daughter languages
- The daughter languages became parent languages to more daughter languages
To make parent and daughter languages easier to understand, linguists like to organize them into a tree diagram, or, simply, a language family tree.
Some of the other well-known branches of the Indo-European family include, among others:
- Celtic languages
- Slavic languages
- Germanic languages
- Baltic languages
- Indo-Iranian languages
- Greek languages
To date, Ethnologue lists as many as 145 language families.
Why Do We Need to Understand Language Families?
By understanding the structure of a language family, we can understand the history of language as a whole.
Language classification may well be a complex science, we know that language families is an excellent starting point for us to start understanding the interrelatedness of human languages and how to communicate effectively on a global level when it comes to the importance of accurate translation and localization.
Further, we can effectively use this knowledge not just to understand the history of languages, but also to understand how the mastery of one language in a language family or group can help us master other languages within the same group. The more closely related two languages are, the easier it is to acquire both in succession.
Most importantly, the easier it is for you to reach a global audience or customer-base and grow your bottom line.
Subscribe for more
Stay up to date with the latest articles, news and translation insights


